- Tool Option In R For Machine Learning
- Tool Option In R For Macbook Pro
- Tool Option In R For Mac Os
- Tool Option In R For Macs
When your computer encounters a serious problem that normal troubleshooting methods can’t fix, you can try installing a fresh copy of your macOS to resolve it. If you want to install the latest macOS version that was previously installed on your computer, just press Command + R when restarting your Mac to pull up the macOS Recovery dialog.
Run R CMD build to make the package file Read 'Writing R Extensions' for more information. The R folder/directory contains each function listed in the call to the skeleton function created as an individual file with the suffix R. E.g., alpha.scale.R, omega.R, etc. Corrections to your code can be done directly to these files. R Tutorial Obtaining R. R is available for Linux, MacOS, and Windows. Software can be downloaded from The Comprehensive R Archive Network (CRAN). After R is downloaded and installed, simply find and launch R from your Applications folder. Entering Commands. R is a command line driven program.
But what happens when the Command + R shortcut doesn’t work? You can still access your macOS Recovery options, but it’s going to be a bit more complicated. This guide will teach you how to reinstall your macOS even if Mac Recovery Mode is not working on your MacBook.
But first, it is important to understand the reasons why the Command + R shortcut may not work.
Reasons Why Command R Is Not Working on Macbook
There are a few reasons why the Command + R combination may not work on your computer, such as:

- Age of your Mac – If you’re using a Mac that’s still running OS X Snow Leopard or older operating system, then your version doesn’t have Recovery Mode. This feature was introduced with the release of OS X Lion in 2011 to allow users to diagnose hardware features and troubleshoot common Mac problems on startup.
- macOS version – If your macOS version is older than Sierra, then the Recovery options you have may not be the same as those running newer versions.
- Faulty keyboard – It is possible that your letter keys are not working.
- Corrupted recovery partition – Your recovery partition may have been corrupted or deleted.
Before we discuss how to access your Recovery mode when Command + R is not working on Macbook, let’s first talk about what this mode is and its functions.
What Is MacBook Recovery Mode?
Not all Mac users know what the Recovery Mode is and what it is for. Many users don’t even know this feature exists. To put it simply, the Recovery Mode is a dedicated partition on your hard drive housing a recovery image and a copy of your macOS installer. This partition is completely independent from the other partitions on your disk that even if you wipe your hard drive clean, it would still be there.
The recovery partition is helpful in extreme cases where you might need to reinstall a fresh copy of your latest macOS or OS X. Even if you format your drive and start from scratch, this partition remains intact and you can still reinstall your macOS, restore from a Time Machine backup , or repair your disk via Recovery Mode.
The Recovery Mode makes troubleshooting a lot easier and faster because all you need to do is press two keys: Command + R. But before you proceed with the solutions below, make sure to back up all your important files and optimize your Mac using an app such as Outbyte MacRepair.
How to Check if Your Mac’s Recovery Partition is Working
The first thing you need to rule out is whether you actually have a recovery partition and if it is working fine.
To boot into your Recovery Drive, follow these instructions:
- Shut down your Mac by clicking the Apple menu and choosing Shut Down.
- Once the computer is turned off, hold down Command + R, then press the Power button.
- Keep holding the Command + R keys until the Apple logo appears. Let go of the keys and wait for the startup process to complete. This may take longer than your usual boot up process, but don’t worry because it’s just loading items from your recovery partition.
- When you see the macOS Utilities window or OS X Utilities for older Macs, then it means your recovery partition is working.
But if your Mac boots into the regular login window or just loads a blank screen, then you don’t have a recovery partition.
You can also use Terminal to verify if you have a recovery partition by following the steps below:
- Launch Terminal via Utilities folder or Spotlight search.
- Type in diskutil list. This will show you a list of all the volumes and partitions on your Mac.
Look for drive with Boot Recovery HD in its name because that’s your recovery partition. If you see it on the list but can’t boot into it for some reason, then the drive could be corrupted. If it’s not on the list, then the drive could have been deleted or you never had it in the first place.
Let’s look at some of the things you can do when Mac Recovery Mode is not working on MacBook.
Method 1: Use Internet Recovery to Reinstall macOS
If you have a corrupted or missing recovery partition, you can still reinstall your macOS or OS X via the Utilities tool. This feature is available for newer Macs, and it allows you to boot directly from an internet connection even without a recovery partition.
To use macOS Internet Recovery:
- Shut down your Mac by clicking the Apple logo > Shut Down.
- Hold down the Command + Option/Alt-R keys, then press the Power button.
- Let go of the keys when you see the spinning globe and the message “Starting Internet Recovery. This may take a while.”
- A progress bar will appear after this message. Wait for it to complete and for the macOS Utilities window to appear.
- Click Reinstall macOS from the options that appear and follow the on-screen instructions.
Take note that Internet Recovery only works with networks using WEP and WPA security. If your network is using a different protocol, we suggest you connect to one that is compatible with the Internet Recovery feature because this method, by far, is the easiest way to reinstall your macOS.
Method 2: Create a USB macOS Bootable Installer
If you have no access to Internet Recovery, you can try creating a bootable macOS installer using a flash drive. You need one with at least 12GB in storage. If you’re using an existing flash drive, make sure to back up all the files in it because this process completely erases all the content of the USB.
The easiest way to create a USB macOS installer is via Terminal. But first, you need to locate the Install files for the macOS version you want to install. Go to your Applications folder and look for the installer files, or you can get them from your Mac App Store under the Purchased tab.
Once you have downloaded the installer, follow these steps to create your bootable drive:
- Connect your flash drive to your computer.
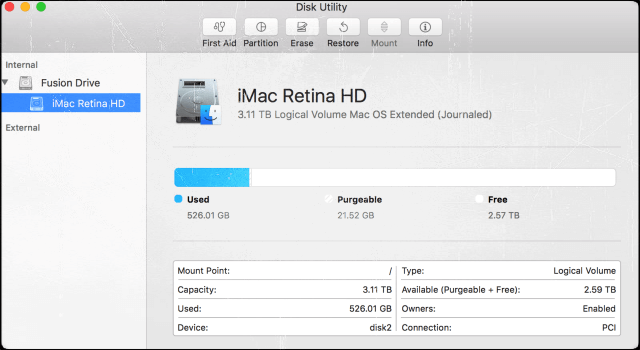
- Launch Disk Utility and select your flash drive. This should be listed under External in the sidebar .
- Click Erase.
- Once the drive has been erased, you’ll see that the name of the drive has been changed to Untitled.
- Launch Terminal and copy the following command, depending on the version you want to reinstall:
- Mojave: sudo /Applications/Install macOS Mojave Beta.app/Contents/Resources/createinstallmedia –volume /Volumes/USB –nointeraction –downloadassets
- High Sierra: sudo /Applications/Install macOS High Sierra.app/Contents/Resources/createinstallmedia –volume /Volumes/MyVolume –applicationpath /Applications/Install macOS High Sierra.app
- Sierra: sudo /Applications/Install macOS Sierra.app/Contents/Resources/createinstallmedia –volume /Volumes/MyVolume –applicationpath /Applications/Install macOS Sierra.app
- El Capitan: sudo /Applications/Install OS X El Capitan.app/Contents/Resources/createinstallmedia –volume /Volumes/MyVolume –applicationpath /Applications/Install OS X El Capitan.app
- Yosemite: sudo /Applications/Install OS X Yosemite.app/Contents/Resources/createinstallmedia –volume /Volumes/MyVolume –applicationpath /Applications/Install OS X Yosemite.app
- Mavericks: sudo /Applications/Install OS X Mavericks.app/Contents/Resources/createinstallmedia –volume /Volumes/MyVolume –applicationpath /Applications/Install OS X Mavericks.app
- Type in your admin password. Next, type in Y and hit Return .
This will erase your hard drive first, and then convert your USB into a bootable installer. Wait for the process to finish, and then use your new bootable installer to reinstall your macOS using the steps below:
- Shut down your Mac while your USB installer is connected.
- Hold down the Option/Alt keys, then press the Power key.
- You’ll see your startup device list with the USB drive highlighted in yellow.
- Choose your bootable drive and hit Return.
- Choose Disk Utility and select your main hard drive.
- Click Erase, then give your drive a name.
- Select Mac OS Extended (Journaled) under Format and GUID Partition Map under Scheme.
- Click Erase > Done.
- Go to Disk Utility > Quit Disk Utility.
- Hit the Install macOS button, then click Continue.
- Follow the installation instructions.
The whole installation process can take around 30 minutes to one hour , so make sure that you have enough battery or your Mac is plugged in to avoid interruptions.
Summary
You can use any of the above methods to reinstall your macOS even without a Recovery partition. However, if your computer is running Snow Leopard or older, you need to install the operating system using the original discs that shipped with your Mac (if you still have them), or purchase them from Apple for $19.99.
See more information about Outbyte and uninstall instructions. Please review EULA and Privacy Policy.
Development Tools and Libraries
CRAN R 4.0.0 builds and higher no longer use any custom compilers and thus this directory is no longer relevant. We now use Apple Xcode 10.1 and GNU Fortran 8.2 from https://github.com/fxcoudert/gfortran-for-macOS/releases.For more details on compiling R, please see alsohttps://mac.R-project.org/tools/Previous tools
The following is provided as support of older versions of R. If you use R 4.0.0 or higher, please disregard and read the top section.R 3.5.0-3.6.3 El Capitan binaries and higer were using more recent Clang compiler and GNU Fortran 6.1 to provide OpenMP parallelization support and C++17 standard features. If you want to compile R packages from sources, please download GNU Fortran binary from the official GNU Fortran Binaries page - in particular OS X 10.11 gfortran 6.1. Alternatively, we are providing a copy here as well as Clang binaries for OS X 10.11 and higher - see below for the download links.
Tool Option In R For Machine Learning
Files:
| clang-8.0.0.pkg (OS X 10.11+, signed, 64-bit) MD5-hash: 664582b0722cb59802cb762b2ad7548b (ca. 482Mb) | Clang 8.0.0 for OS X 10.11 and higher, release build for x86_64, signed package, installs into /usr/local/clang8. To be used with El Capitan builds of R 3.7.0 and higher. It is an installer version of the official LLVM released binaries only modified to use the path above. |
| clang-7.0.0.pkg (OS X 10.11+, signed, 64-bit) MD5-hash: cef3fd2a5c165d00f9941f64ea4024f7 (ca. 463Mb) | Clang 7.0.0 for OS X 10.11 and higher, release build for x86_64, signed package, installs into /usr/local/clang7. To be used with El Capitan builds of R 3.6.x. It is an installer version of the official LLVM released binaries only modified to use the path above. |
| clang-6.0.0.pkg (OS X 10.11+, signed, 64-bit) MD5-hash: c29700c4e7b2914073ef7e741eb105bc (ca. 418Mb) | Clang 6.0.0 for OS X 10.11 and higher, static build for x86_64, signed package, installs into /usr/local/clang6. To be used with El Capitan builds of R 3.5.x. |
| gfortran-6.1.pkg (OS X 10.11+, signed, 64-bit) MD5-hash: 201026216e8b373d9cd2efc0cc474bb8 (ca. 73Mb) | GNU Fortran 6.1 for OS X 10.11 and higher - a copy from GFortranBinaries pages for x86_64, signed package, installs into /usr/local/gfortran (identical content, re-packaged to a flat Installer package and signed). To be used with El Capitan builds of R. |
| The following binaries are obsolete and only provided for historical reasons | |
| gfortran-4.2.3.pkg (OS X 10.5+, signed, 64-bit driver) MD5-hash: 8783f803038abe6487a362ad5b8995ea (ca. 27MB) gfortran-4.2.3.dmg (OS X 10.4, 32-bit driver) MD5-hash: 9551fc46f55537dd1db581154daf27ef (ca. 27MB) | Universal GNU Fortran 4.2.3 for Mac OS X 10.4 and higher. It is necessary in order to build R packages from sources that contain Fortran code. Unlike many other builds, this is a fully universal build of GNU Fortran that uses Apple's driver and supports all target architectures (i386, ppc, x86_64 and ppc64). As such it fully supports compilation into fat files like gfortran -arch i386 -arch ppc -arch x86_64 -arch ppc64 t.f -o ton both Intel Macs and PowerPC Macs (32- and 64-bit). Dependent libraries are fat as well, avoiding problems known from other Fortran builds (such as those from HPC). It installs in /usr/local and comes with an uninstall-script. |
| tcltk-8.5.5-x11.pkg (OS X 10.5+, signed) MD5-hash: e7c406d91762ffdc4539b23c5b5a3ab4 (ca. 9MB) tcltk-8.5.5-x11.dmg (OS X 10.4) MD5-hash: c32dda1b9f2c2776a02cec4e03befc76 (ca. 9MB) | Universal build of Tcl/Tk 8.5.5 for X11 (32-bit and 64-bit). This library is necessary in order to use the tcltk R package (for R 2.8.0 - 2.15.3 only!). It installs in /usr/local. Requires Mac OS X 10.4 (Tiger) or higher for 32-bit R and Mac OS X 10.5 (Leopard) or higher for 64-bit R. NOTE: R 3.0.0 and higher comes bundled with Tck/Tk 8.6.0 so you do not need this package |
For other (optional) 3rd party libraries for development see http://mac.R-project.org/libs/. The devpack has been superseded by those libraries. For R you may want to download and install libpng, libjpeg, readline, freetype, fontconfig, pixman and cairo.
Source code for all 3rd party libraries can be found at http://mac.R-project.org/src/
The dependency libraries used by the CRAN macOS build system are now managed by build recipes. Package authors wishing to add static dependendies can create a pull request to add a dependency.
Subdirectories:
| old | Previous versions of tools as supplied with legacy R versions. |
You may also want to read the R FAQ and R for Mac OS X FAQ. For discussion of Mac-related topics and reporting Mac-specific bugs, please use the R-SIG-Mac mailing list.
Tool Option In R For Macbook Pro
Information, tools and most recent daily builds of the R GUI, R-patched and R-devel can be found at http://mac.R-project.org/. Please visit that page especially during beta stages to help us test the Mac OS X binaries before final release! The page also contains links to experimental builds as such 64-bit R for OS X.
Tool Option In R For Mac Os
Link to corresponding sources: http://mac.R-project.org/src/
Tool Option In R For Macs
Last modified: 2020/04/24, by Simon Urbanek
